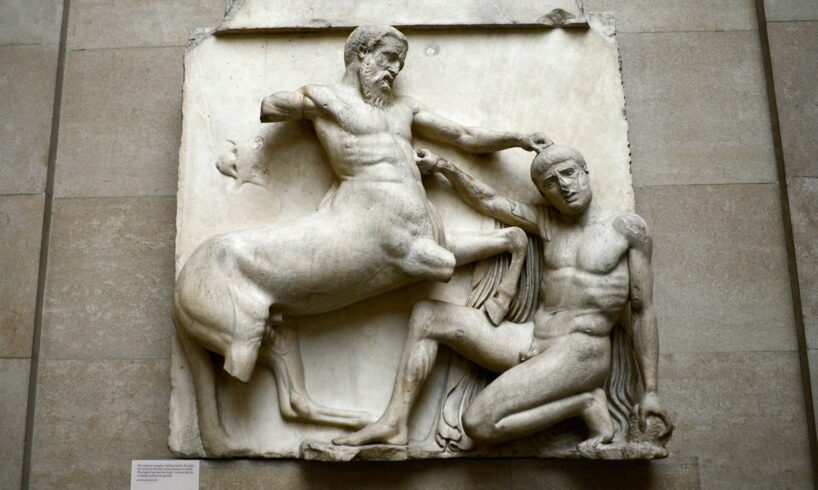
A new documentary proves “beyond any shadow of a doubt” that the Elgin Marbles were stolen, according to its director.
David Wilkinson claims The Marbles settles one of the most divisive debates in cultural heritage: whether 19th-century diplomat Lord Elgin legally acquired the Parthenon Sculptures, better known as the Elgin Marbles.
The film revisits how the sculptures were removed from the Parthenon in Athens while Greece was under Ottoman rule – and ended up in London.
It argues that Lord Elgin did not legally acquire the artefacts – and instead, it amounts to “the greatest heist in art history”.
Image:
Reuters file pic
Actor Brian Cox, historian Dominic Selwood and solicitor Mark Stephens are among those who appear in the documentary.
The British government bought the sculptures from Lord Elgin and installed them into the trusteeship of the British Museum, where they have remained for 200 years.
“He needed the money from the British government to pay for all the bribes he’d given to members of the Ottoman Empire,” Wilkinson says of the transaction.
“Lord Elgin did sell them … but the question becomes, did Lord Elgin actually have the right to purchase them?”
Image:
PA file pic
Classical archaeologist Mario Trabucco della Torretta dismisses Wilkinson’s claims.
“The allegation of bribery to obtain the Marbles is just wrong in historical terms,” he told Sky News.
Torretta was the key architect behind a joint letter that included former prime minister Liz Truss, historian Dr David Starkey and Sir John Redwood – alleging the British Museum is part of a “covert” and “accelerating campaign” to return the Elgin Marbles to Greece.
Responding to Wilkinson’s claims of bribery, he added: “The only reference to ‘presents’ comes years after the start of the removals … do people presume that they run a ‘bribe now, pay later’ scheme back then in Constantinople?”
One of the most contentious points in the debate is the legitimacy of an Ottoman permission document known as a “firman”, which is claimed to have authorised Lord Elgin removing the items from Greece.
There is only an Italian text referred to as a translation of this document.
Image:
David Wilkinson
Wilkinson said: “It was normal practice at the time that a copy would be kept in what was then Constantinople, and another copy would have been sent off to Athens.
“There would be a record in Istanbul and the Turks have gone through it in great detail over many decades and they can find nothing.”
Speaking to Sky News in 2024, Dr Zeynep Boz – head of combatting illicit trafficking for Turkey’s culture ministry – said there is no proof of the firman in the Ottoman archive.
“Despite extensive archival research, no such firman has been found. It is even difficult to call this document a translation when the original is not available,” she said at the time.
Torretta offers an explanation: “Burning the Ottoman governor’s archive was one of the first acts of the Greek revolution.”
Image:
Reuters file pic
While the arguments are not new, The Marbles also examines how other institutions have handled similar restitution cases.
In the film, Cox says if the marbles would have gone back to Athens already if they had found their way to Edinburgh and not London.
Back in 2023, the National Museum of Scotland returned The House Of Ni’isjoohl memorial pole to Canada.
Meanwhile, Glasgow’s Kevingrove Art Gallery Museum returned a shirt to the South Dakota Cultural Heritage Center in the US.
And when it comes to the Parthenon Sculptures – Germany’s Heidelberg University and The Vatican have both returned fragments to Greece.
1:51
Dec 2024: Elgin Marbles ‘belong in the UK’
The British Museum Act 1963 prevents treasures being legally given away by the British Museum.
The government has repeatedly it has no plans to change existing policy on restitution, and that it is up to the trustees of the museum to decide.
A spokesperson for the British Museum repeated a statement given to Sky News in July: “Discussions with Greece about a Parthenon Partnership are ongoing and constructive.”
The documentary scrutinises the ethics of foreign national treasures that were taken and are now housed in Western museums, but as it stands the institutional and governmental answers don’t appear to be changing.
The Marbles is in UK and Irish cinemas from today.